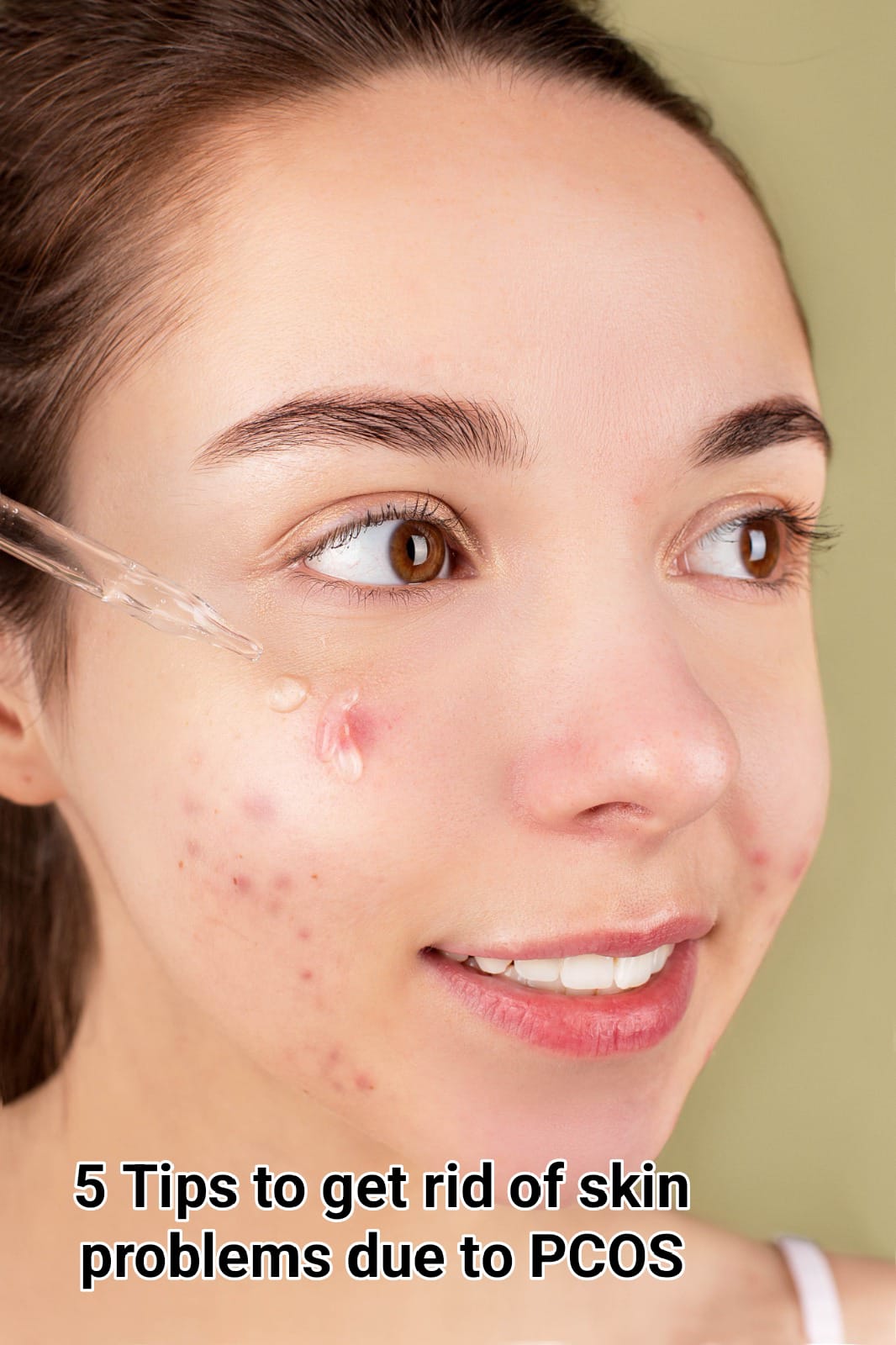
Female infertility refers to a woman’s failure to conceive a child or carry a pregnancy to term despite having frequent, unprotected sexual intercourse for an extended period of time (typically a year or more, depending on age and other circumstances). Female infertility is a physical disorder with multiple underlying causes that can create emotional and psychological discomfort in people who suffer from it.
Causes of female infertility:
Four common causes of female infertility include:
- Ovulatory disorders: When ovulation, the critical process of egg release, becomes erratic or stops entirely, it can lead to female infertility concerns. Complex disorders such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hypothalamus dysfunction, and premature ovarian failure (early menopause) can disrupt the normal ovulation patterns required for healthy pregnancy.
- Fallopian Tube Blockage or Damage: The intricate network of fallopian tubes transports eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Unfortunately, obstructions or damage in these tubes, which are frequently caused by illnesses like pelvic inflammatory disease, the existence of endometriosis, or previous surgical treatments, can effectively operate as barriers. They impede fertilization and causes female infertility.

- Uterine Abnormalities: The structural integrity of the uterus is critical in reproductive health. Exceptions to the norm, such as the development of uterine fibroids, polyps, or adhesions that generate scar tissue, have the potential to disrupt the delicate dance of embryo implantation or the orderly progression of pregnancy. These uterine abnormalities might be substantial obstacles on the road to conception nothing but female infertility.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a disorder that causes tissue similar to the uterine lining to expand beyond its intended bounds, posing a complex challenge like female infertility issues. This growth frequently includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the surrounding pelvic landscape. Inflammation, scar tissue formation, and adhesion creation characterize the aftermath, all of which contribute to an environment that impedes fertility and conception.
The cause of female infertility is frequently determined using a mix of medical history, physical exams, hormone level tests, imaging techniques (such as ultrasounds), and, in some cases, small surgical procedures. Treatment options differ according to the underlying cause. Lifestyle adjustments, hormone therapy, surgery to rectify structural abnormalities, assisted reproductive technologies (such as in vitro fertilization or IVF), and other treatments may be included.
How PCOS causes female infertility?
Two major causes among the four such as Ovulatory disorders and blockage in fallopian tube mentioned above are due to PCOS. PCOS is a prevalent hormonal condition that affects a large number of women of reproductive age. PCOS causes female infertility in many other ways by interfering with the normal ovulation process and altering egg maturation. Here’s how PCOS can contribute to infertility:
- Imbalance of Hormones: Women with PCOS often have greater amounts of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone. Elevated androgen levels can disrupt the hormonal balance required for ovulation and interfere with normal ovarian function which might trigger female infertility.
- Insulin Resistance: Many women with PCOS have insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells do not respond to insulin adequately. Insulin resistance can result in increased insulin production and blood insulin levels. Elevated insulin levels can encourage the ovaries to create more androgens, causing ovulation and the menstrual cycle to be disrupted which further effects women’s reproductive system causing female infertility issues.
- Anovulatory Cycles: Anovulatory cycles are typical in women with PCOS, in which the ovaries do not release a mature egg. There is no egg accessible for fertilization by sperm in the absence of ovulation, making conception impossible.
- Cyst Formation: While the term “polycystic ovary syndrome” implies the presence of cysts on the ovaries, they are not actual cysts, but rather immature follicles that fail to mature and produce eggs. These follicles can build up and cause hormonal abnormalities and irregular periods which further effects female infertility.

- Cervical Mucus Changes: PCOS can cause changes in cervical mucus, making it thicker and less conductive to sperm movement. This can make it difficult for the sperm to reach and fertilize the egg. There by resulting in female infertility.
- Endometrial Abnormalities: PCOS can cause alterations in the uterine lining (endometrium), making it less amenable to fertilized embryo implantation. Even if fertilization occurs, the embryo may have difficulty implanting and establishing a pregnancy.
Root causes of PCOS:
To treat a health problem or to arrive at a solution for any other problem one should be aware of the root cause and not just the symptoms. Because if we treat the problem basing the symptoms then it will be a temporary as the root cause doesn’t go away. Hence knowing the root cause and treating it from underneath is important if you want permanent solution.
So knowing the root causes of PCOS is important to treat it permanently.
Basically there are ten modern lifestyle root causes for hormonal imbalances related to PCOS:
Hormonal imbalances, which are created by ten fundamental aspects of contemporary lifestyle, are the primary cause of PCOS. Now let’s see the root causes of PCOS in order to reverse it.
Food related root Causes:
- Food toxicity: Foods high in additives, preservatives, and chemicals can contribute to hormone imbalances by altering the endocrine system.
- Inflammation: Diets high in processed foods, sweets, and bad fats can cause the body to become more acidic and inflammatory, disrupting the body’s hormonal balance.
- A lack of micronutrients in our diet: Because these nutrients are essential for a variety of hormonal actions, a lack of critical vitamins and minerals may interfere with hormone balance.
- Insulin resistance: Meals with a high glycemic index can promote insulin resistance: Eating meals with a high glycemic index can create insulin resistance, which affects hormone levels, particularly insulin and androgens.
- Excess male hormones: Eating foods high in chemicals, steroids, or hormone-disrupting components may result in an increase in male hormones (androgens), which may contribute to hormonal disorders.
Exercise Related Causes:
- Sedentary lifestyle: It involves spending most of one’s time sitting down: Excessive sitting and a lack of exercise can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalance.
- Excess body fat over the ovaries: Insulin resistance and inflammation brought on by excess body fat, especially in the area of the belly, may be linked to hormonal irregularities.
- Lack of muscle mass: Lack of physical exercise and muscle mass can affect insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance in general.
Sleep related root causes:
- Poor sleep quality (Lack of Deep Sleep): Poor or insufficient sleep can throw off the body’s hormonal balance, especially the hormones that control hunger and stress (leptin and ghrelin).
Stress related root causes:
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged exposure to high levels of stress can cause the deregulation of various hormones, including cortisol, upsetting the body’s overall hormonal balance.
Now as we understood the root causes we can now treat PCOS naturally by adapting few strategies that not only treat PCOS but also helps us in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
However overcoming these is not impossible. One can definitely reverse the condition by adopting the 5 pillar strategy which is known for treating PCOS naturally.
The 5 pillar strategy to reverse PCOS naturally:
The below 5 pillar strategy is based on natural methods which doesn’t involve any side effects and which will result in permanent cure of PCOS.
- Eat Right: Embrace living, water-rich, whole, plant-based foods that nurture our genetic potential. By opting for local and seasonal choices, we honor nature’s wisdom. Eliminating packaged and processed foods liberates us from epigenetic imprints, elevating our hormonal health.
- Move More: Embark on a journey of holistic lifestyle changes, where staying active transcends mere exercise. Embracing constant movement throughout the day optimizes epigenetic expression, igniting hormonal balance.
 Engage in pleasurable physical activities, dance, or even mindful walks to unlock the power of epigenetic triggers.
Engage in pleasurable physical activities, dance, or even mindful walks to unlock the power of epigenetic triggers.
- Breathe Aware: As we deepen our understanding of Pranayama, the science of breath, we access a profound gateway to support gland function and harmonize hormones. Harnessing the breath’s epigenetic influence, we transcend the ordinary and elevate our hormonal well-being.
- Sleep Better: Unlock the secrets of deep sleep, a transformative practice for healing and regeneration. With the art of Yog Nidra, we embrace epigenetic potential, unearthing hormonal harmony in the realm of dreams. Rejuvenate your entire being through this exquisite dance with the epigenetic clock.
- Mind Free: Journey into the realm of emotions, thoughts, and stress resilience, where journaling, gratitude, and emotional practices become our guiding compass. Embracing epigenetic intelligence, we shift our narrative from stress to serenity, empowering our hormonal landscape.
Addressing underlying problems that can prevent pregnancy and cause female infertility, such as hormone imbalances, structural abnormalities, or medical illnesses, is a key component in treating reproductive difficulties.
Hence adopting the above 5 pillar strategy may help to balance the hormones which help to reverse PCOS which is the cause of female infertility. Achieving a healthy pregnancy and child can be a goal for both people and couples who receive effective reproductive treatment.